
Why should you choose Peptamen®?
Peptamen® is a scientifically proven nutritional solution that meets patients’ specific needs. Its proven effectiveness makes it a reliable choice for providing high-quality care and improving patients' overall health.

What is the difference between Peptamen® and other formulas?
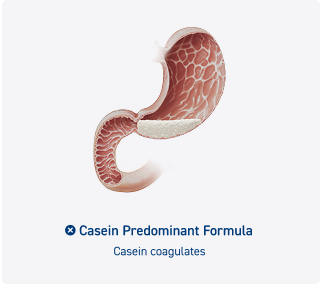
Peptamen® distinguishes itself from other enteral nutrition products through its unique formulation of 100% hydrolyzed whey protein and medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), enhancing digestibility and tolerance. It is backed by extensive clinical evidence, demonstrating lower gastrointestinal intolerance compared to standard formulas.1-3 Additionally, Peptamen® offers a versatile range of specialized nutritional solutions tailored to the needs of patients with gastrointestinal disorders, while also being cost-effective in reducing care expenses associated with enteral feeding intolerance.3
How can Peptamen® support your treatment strategies?
1. Clinically proven digestibility and absorption
Peptamen® utilizes hydrolyzed whey protein and MCTs to improve gastrointestinal tolerance (GI) in patients with compromised digestive systems. This unique formulation minimizes the risk of feeding intolerance, allowing for more effective nutritional support and quicker energy replenishment. The readily absorbed MCTs provide an ideal energy source for patients who require rapid energy restoration.4
HYDROLYZED 100% WHEY PROTEIN improves GI tolerance5-6 and digestive function6-11
Promotes faster
gastric emptying
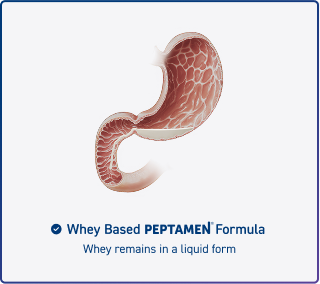
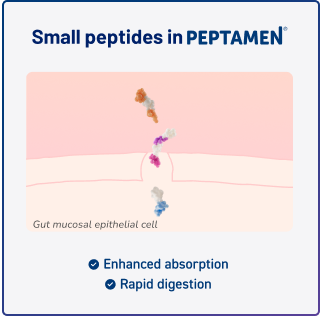
Enhances protein
absorption
MEDIUM CHAIN TRIGYLERIDES provide optimal lipid nutrition
as they are absorbed directly into the bloodstream12-15
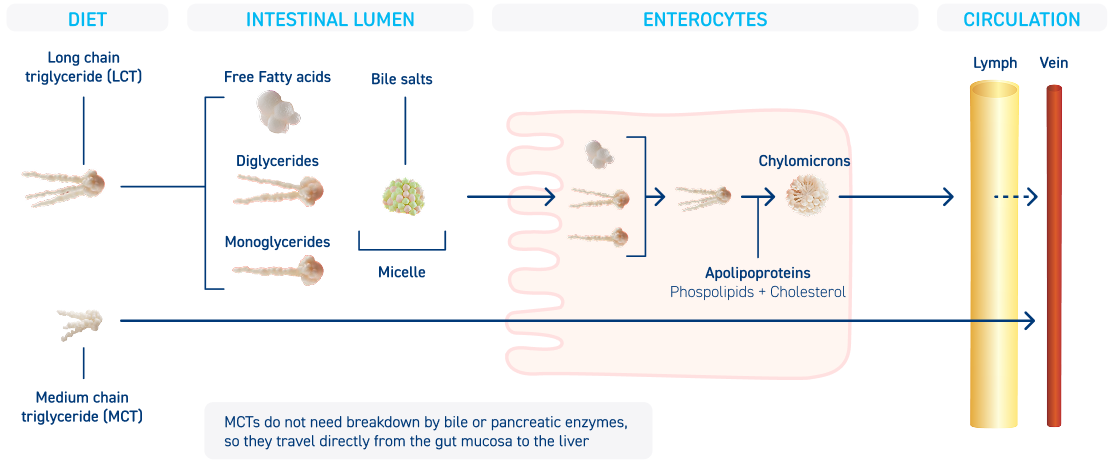

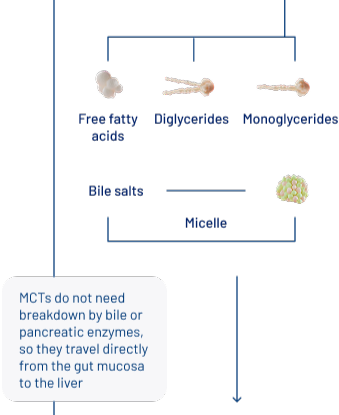
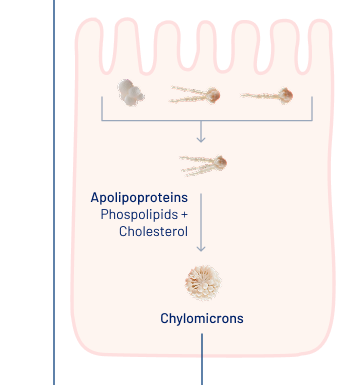
Learn more about the importance of WHEY PROTEIN and MCT
2. Clinically proven health outcomes
With over 35 years of clinical experience and more than 100 published studies, Peptamen® has a strong foundation of evidence demonstrating improved nutritional status, reduced complications, and shorter hospital stays across diverse patient populations.
Peptamen® reduces GI intolerance making it a valuable option for patients requiring enteral nutrition, especially in acute and home care1,3.
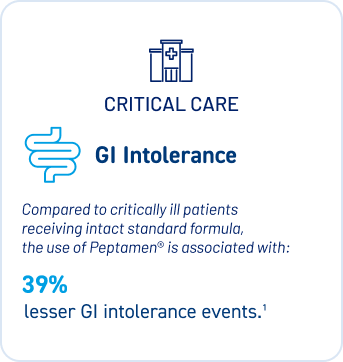
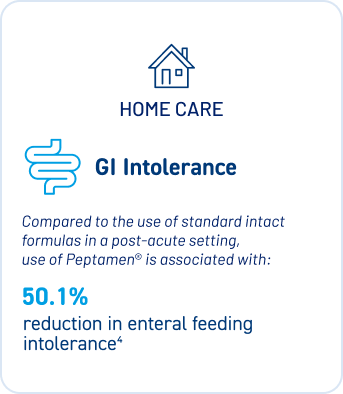
3. Tailored Nutritional Solutions
The Peptamen® product line offers a variety of formulations with different protein levels and caloric densities, allowing healthcare providers to customize nutrition plans based on individual patient needs and clinical conditions.
- Impaired GI function
- Early enteral feeding
- Transition from Parenteral Nutrtion
- Malnutrition
- Malabsorption
- IBD
- Critically ill
- Cerebral Palsy
- Chronic Diarrhoea
- After GI surgery
- Chronic pancreatitis

ONS
TUBE FEEDING
4. Cost-Effective Alternative
Peptamen® reduces gastrointestinal complications and the need for additional interventions, offering a cost-effective alternative to standard nutritional formulas that benefits both healthcare systems and patient outcomes.3
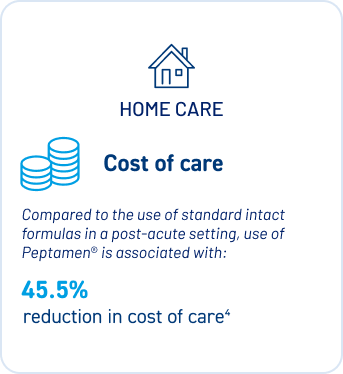
Who will benefit from using Peptamen®?
Peptamen® is specifically indicated for patients with gastrointestinal disorders who necessitate
targeted
nutritional intervention due to impaired digestion and nutrient absorption.
Our malabsorption index will help you to identify individuals with malabsorption and provide guidance on
selection of enteral feeds.
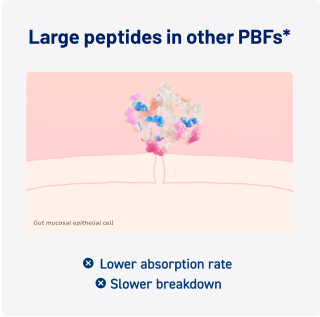
*Peptide-based formulas
References:
1. Raphaeli O et al. Clin NutrESPEN 2024;63:1037. 2. LaVallee C, et al. J ParenterEnteral Nutr2021;45(8):1729-1735. 3. Elfadil O, et al. J ParenterEnteral Nutr2023;47(suppl2):S18-S20. 4. Elfadil O, et al. Nutr Clin Pract2023;38(2), 318-328. 5. Fried M, et al. J Pediatr1992;120:569-572. 6. Bendtsen LQ, et al. Adv Nutr2013;4(4):418-438. 7. Anthony JC, et al. J Nutr2001;131(3):856S-60S. 8. Ha E and Zemel MB. J Nutr Biochem2003;14(5):251-258. 9. Katsanos CS, et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab2006;291(2):E381-E387. 10. Wu G, et al. J Nutr2004;134(3):489-492. 11. Marshall K. Altern Med Rev 2004;9(2):136-156. 12. Ruppin DC and Middleton WR. Drugs1980;20(3):216-224. 13. Qiu C, et al. J Parenter Ent Nutr 2017;41(5):785-795. 14. Nugent S, et al. OCL 2016;23(1):0110. 15. Bach AC and Babayan VK. Am Clin Nutr1982;36(5):950-962.
















